Tutorial 5: SQL
By Chaofa Gao
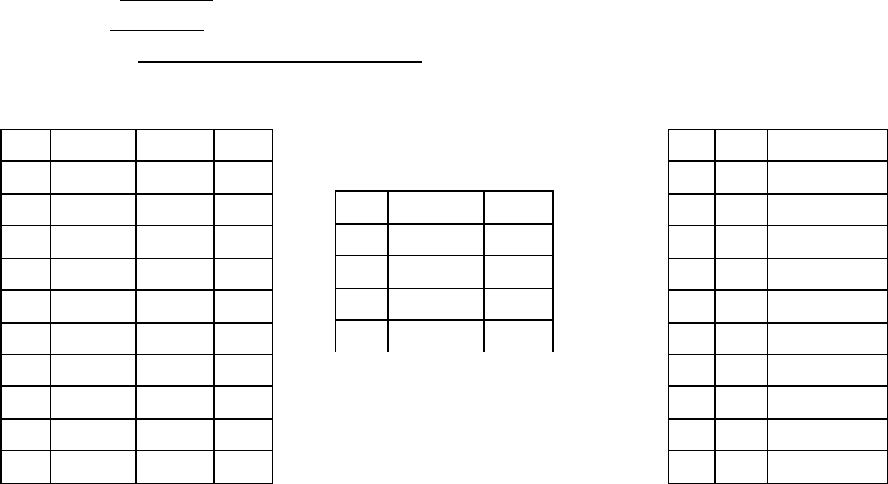
Tables used in this note:
Sailors(sid: integer, sname: string, rating: integer, age: real);
Boats(bid: integer, bname: string, color: string);
Reserves(sid: integer, bid: integer, day: date).
Sailors Reserves
Boats
Figure 1: Instances of Sailors, Boats and Reserves
1. Create the Tables:
CREATE TABLE sailors ( sid integer not null,
sname varchar(32),
rating integer,
age real,
CONSTRAINT PK_sailors PRIMARY KEY (sid) );
CREATE TABLE reserves ( sid integer not null,
bid integer not null,
day datetime not null,
CONSTRAINT PK_reserves PRIMARY KEY (sid, bid, day),
FOREIGN KEY (sid) REFERENCES sailors(sid),
FOREIGN KEY (bid) REFERENCES boats(bid) );
Sid
Sname
Rating
Age
22
Dustin 7 45
29
Brutus 1 33
31
Lubber
8 55.5
32
Andy 8 25.5
58
Rusty 10 35
64
Horatio
7 35
71
Zorba 10 16
74
Horatio
9 40
85
Art 3 25.5
95
Bob 3 63.5
sid
bid
day
22
101
1998-10-10
22
102
1998-10-10
22
103
1998-10-8
22
104
1998-10-7
31
102
1998-11-10
31
103
1998-11-6
31
104
1998-11-12
64
101
1998-9-5
64
102
1998-9-8
74
103
1998-9-8
bid
bname color
101
Interlake
blue
102
Interlake
red
103
Clipper green
104
Marine red

2. Insert Data
INSERT INTO sailors
( sid, sname, rating, age )
VALUES ( 22, 'Dustin', 7, 45.0 )
INSERT INTO reserves
( sid, bid, day )
VALUES ( 22, 101, '1998-10-10')
Note the date can have one of the following formats:
yyyy-mm-dd, mm-dd-yyyy and mm/dd/yyyy
In addition, DB2 allows to parse the date attribute using its month(), year() and day() functions.
e.g. select * from reserves where year(day) = 1998 and month(day) = 10
3. Simple SQL Query
The basic form of an SQL query:
SELECT [DISTINCT] select-list
FROM from-list
WHERE qualification
Ex1: Using DISTINCT
SELECT sname, age
FROM sailors
or
SELECT S.sname, S.age
FROM sailors S
SELECT DISTINCT S.sname, S.age
FROM sailors AS S
Ex2. Find all information of sailors who have reserved boat number 101.
SELECT S.*
FROM Sailors S, Reserves R
Sname age
Dustin 45
Brutus 33
Lubber 55.5
Andy 25.5
Rusty 35
Horatio
35
Zorba 16
Horatio
35
Art 25.5
Bob 63.5
sname age
Andy 25.5
Art 25.5
Bob 63.5
Brutus 33
Dustin 45
Horatio
35
Lubber
55.5
Rusty 35
Zorba 16
WHERE S.sid = R.sid AND R.bid = 103
Or without using the range variables, S and R
SELECT Sailors.*
FROM Sailors, Reserves
WHERE Sailors.sid = Reserves.sid AND Reserves.bid = 103
* can be used if you want to retrieve all columns.
Ex3. Find the names of sailors who have reserved a red boat, and list in the order of age.
SELECT S.sname, S.age
FROM Sailors S, Reserves R, Boats B
WHERE S.sid = R.sid AND R.bid = B.bid AND B.color = ‘red’
ORDER BY S.age
ORDER BY S.age [ASC] (default)
ORDER BY S.age DESC
Ex4. Find the names of sailors who have reserved at least one boat.
SELECT sname
FROM Sailors S, Reserves R
WHERE S.sid = R.sid
The join of Sailors and Reserves ensure that for each select sname, the sailor has made some
reservation.
Ex5. Find the ids and names of sailors who have reserved two different boats on the same day.
SELECT DISTINCT S.sid, S.sname
FROM Sailors S, Reserves R1, Reserves R2
WHERE S.sid = R1.sid AND S.sid = R2.sid
AND R1.day = R2.day AND R1.bid <> R2.bid
Ex6. Using Expressions and Strings in the SELECT Command.
SELECT sname, age, rating + 1 as sth
FROM Sailors
WHERE 2* rating – 1 < 10 AND sname like ‘B_%b’
SQL provides for pattern matching through LIKE operator, along with the use of symbols:
% (which stands for zero or more arbitrary characters) and
_ (which stands for exactly one, arbitrary, characters)
4. Union, Intersect and Except
Note that Union, Intersect and Except can be used on only two tables that are union-compatible,
that is, have the same number of columns and the columns, taken in order, have the same types.
Ex7. Find the ids of sailors who have reserved a red boat or a green boat.
SELECT R.sid
FROM Boats B, Reserves R
WHERE R.bid = B.bid AND B.color = ‘red’
UNION
SELECT R2.sid
FROM Boats B2, Reserves R2
WHERE R2.bid = B2.bid AND B2.color = ‘green’
The answer contains: SID----------22 31 64 74
The default for UNION queries is that duplicates are eliminated. To retain duplicates, use
UNION ALL.
Replace UNION with UNION ALL. The answer contains: 22 31 74 22 31 64 22 31
Replace UNION with INTERSECT. The answer contains: 22 31.
Replace UNION with EXCEPT. The answer contains just the id 64.
6. Nested Query
IN and NOT IN
EXISTS and NOT EXISTS
UNIQUE and NOT UNIQUE
op ANY
op ALL
EX8: Find the names of sailors who have reserved boat 103.
SELECT S.sname
FROM Sailors S
WHERE S.sid IN ( SELECT R.sid
FROM Reserves R
WHERE R.bid = 103 )
The inner subquery has been completely independent of the outer query.
(Correlated Nested Queries)
SELECT S.sname
FROM Sailors S
WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT *
FROM Reserves R
WHERE R.bid = 103
AND R.sid = S.sid )
The inner query depends on the row that is currently being examined in the outer query.
EX9: Find the name and the age of the youngest sailor.
SELECT S.sname, S.age
FROM Sailors S
WHERE S.age <= ALL ( SELECT age
FROM Sailors )
EX10: Find the names and ratings of sailor whose rating is better than some sailor called Horatio.
SELECT S.sname, S.rating
FROM Sailors S
WHERE S.rating > ANY ( SELECT S2.rating
FROM Sailors S2
WHERE S2.sname = ‘Horatio’ )
Note that IN and NOT IN are equivalent to = ANY and <> ALL, respectively.
EX11: Find the names of sailors who have reserved all boats.
SELECT S.sname
FROM Sailors S
WHERE NOT EXISTS ( ( SELECT B.bid
FROM Boats B)
EXCEPT
( SELECT R.bid
FROM Reserves R
WHERE R.sid = S.sid ) )
An alternative solution:
SELECT S.sname
FROM Sailors S
WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT B.bid
FROM Boats B
WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT R.bid
FROM Reserves R
WHERE R.bid = B.bid
AND R.sid = S.sid ) )
7. Aggregation Operators
COUNT ([DISTINCT] A): The number of (unique) values in the A column.
SUM ([DISTINCT] A): The sum of all (unique) values in the A column.
AVG ([DISTINCT] A): The average of all (unique) values in the A column.
MAX (A): The maximum value in the A column.
MIN (A): The minimum value in the A column.
EX12: Count the number of different sailor names.
SELECT COUNT( DISTINCT S.sname )
FROM Sailors S
EX13: Calculate the average age of all sailors.
SELECT AVG(s.age)
FROM Sailors S
EX14: Find the name and the age of the youngest sailor.
SELECT S.sname, S.age
FROM Sailors S
WHERE S.age = (SELECT MIN(S2.age)
FROM Sailors S2 )
SELECT [DISTINCT] select-list
FROM from-list
WHERE qualification
GROUP BY grouping-list
HAVING group-qualification
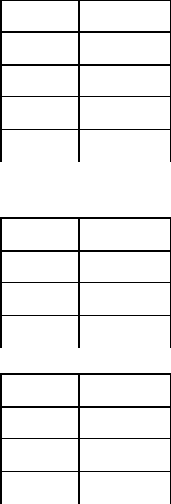
EX15: Find the average age of sailors for each rating level.
SELECT S.rating, AVG(S.age) AS avg_age
FROM Sailors S
GROUP BY S.rating
Rating
avg_age
1 33
3 44.5
7 40
8 40.5
9 35
10 25.5
EX16: Find the average age of sailors for each rating level that has at least two sailors.
SELECT S.rating, AVG(S.age) AS avg_age
FROM Sailors S
GROUP BY S.rating
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
EX16: An example shows difference between WHERE and HAVING:
SELECT S.rating, AVG(S.age) as avg_age
FROM Sailors S
WHERE S.age >=40
GROUP BY S.rating
SELECT S.rating, AVG(S.age) as avg_age
FROM Sailors S
GROUP BY S.rating
HAVING AVG(S.age) >= 40
5. NULL value and OUTER JOIN
In the presence of null values, any row that evaluates to false or to unknown is eliminated
The two rows are duplicates if corresponding columns are either equal, or both contain null.
(If we compare two null values using =, the result is unknown)
The arithmetic operation +, -, * and / all return null if one of their arguments is null.
Count(*) handle null values just like other values. All the other aggregate operations (COUNT, SUM,
AVG, MAX, MIN, and variations using DISTINCT) simply discard null values
After: INSERT INTO sailors
( sid, sname, rating, age )
VALUES ( 99, 'Dan', null, 48.0 ) ,
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Sailors will return 11
SELECT COUNT(rating) FROM Sailors will return 10
SELECT COUNT(age) FROM Sailors will return 11
Rating
avg_age
3 44.5
7 40
8 40.5
10 25.5
Rating
avg_age
3 63.5
7 45
8 55.5
Rating
avg_age
3 44.5
7 40
8 40.5

An example of OUTER JOIN:
SELECT sailors.sid, sailors.sname, reserves.bid
FROM sailors LEFT OUTER JOIN reserves ON reserves.sid = sailors.sid
ORDER BY sailors.sid
sid
sname bid
22
Dustin 101
22
Dustin 102
22
Dustin 103
22
Dustin 104
29
Brutus
31
Lubber
102
31
Lubber
103
31
Lubber
104
32
Andy
58
Rusty
64
Horatio
101
64
Horatio
102
71
Zorba
74
Horatio
103
85
Art
95
Bob
99
Dan
